Explore over 500,000 Images in my personal collection
real images | real history | no AI
|
|

- Code Number:
- ARSV01P11_11B.1713
- Title:
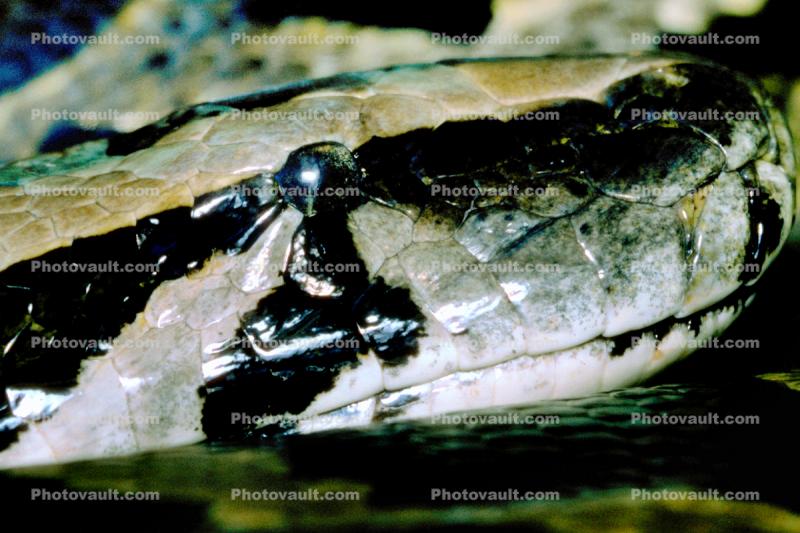
- Burmese Python, (Python molurus bivittatus), Pythonidae, constrictor
- Distribution: Indo-China, China, Indonesia Among the largest pythons, Burmese Pythons can grow to a length of six meters (20 feet), with almost 400 sets of ribs. The largest ones are always female. Burmese Pythons are typically 18 inches to 24 inches long at birth. The female is capable of depositing and incubating up to 100 eggs. The female will gather the eggs together and coil herself around them to keep them warm. She has the ability to raise her own body temperature and does so by making her muscles tremble. The Burmese Python is the only snake who is capable of doing this and the increased body heat helps to keep the eggs warm enough to develop properly.
The eggs hatch in 55-60 days. Although the female will never leave the eggs to eat, once they are hatched the baby pythons are on their own. Pythons kill by constriction, crushing their prey. In the wild, their diet is extremely diverse. They've been reported to eat such things as birds, rats, monkeys, deer and even porcupines! The prey is swallowed whole and digested while the python basks in the sun, which keeps its body temperature high enough to be able to digest properly. Burmese Pythons are able to swallow their prey whole because of their hinged jaw which actually separates and allows them to intake something that is five times as wide as its head. Even though they are often docile in captivity, they make poor pets because of their huge size and unpredictable behavior.
Kingdom: Animalia
Kingdom: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Class: Reptilia
Order: Squamata
Suborder: Serpentes
Family: Pythonidae
Genus: Python
Species: Python molurus
Subspecies: Python molurus bivittatus
Kuhl, 1820 - Keywords:
- Image by:
- Wernher Krutein
- Caption Disclaimer
Rights Managed: Calculate Price